What is DevOps?
.
DevOps is a combination of "Development" (software creation) and "Operations" (managing and deploying software). It's a way of working that emphasizes collaboration between software developers and IT operations teams to create, test, and deliver software faster and more reliably. The goal is to streamline processes, reduce errors, and deliver better software to customers.
.
Think of it as creating a smooth assembly line for software. Instead of working in silos, teams work together throughout the software's lifecycle—planning, coding, building, testing, deploying, and maintaining.
.
Key Principles of DevOps:
.
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks like testing or deployment.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Making frequent, small updates to software instead of big, infrequent ones.
- Collaboration: Breaking down walls between development and operations teams.
- Monitoring: Keeping a constant eye on performance and fixing issues quickly.
.
Common Tools Used in DevOps:
.
1. Version Control: Tools like Git and GitHub to track changes in code.
2. CI/CD Pipelines: Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, or CircleCI to automate testing and deployment.
3. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Tools like Terraform and Ansible to manage infrastructure programmatically.
4. Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes for creating and managing containers (lightweight environments for apps).
5. Monitoring & Logging: Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, Splunk, and New Relic to monitor software and infrastructure performance.
6. Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for hosting and managing applications.
____
In short, DevOps is about working smarter, not harder, to ensure better software with fewer hiccups. If you want to dive deeper into any part of it, let me know!
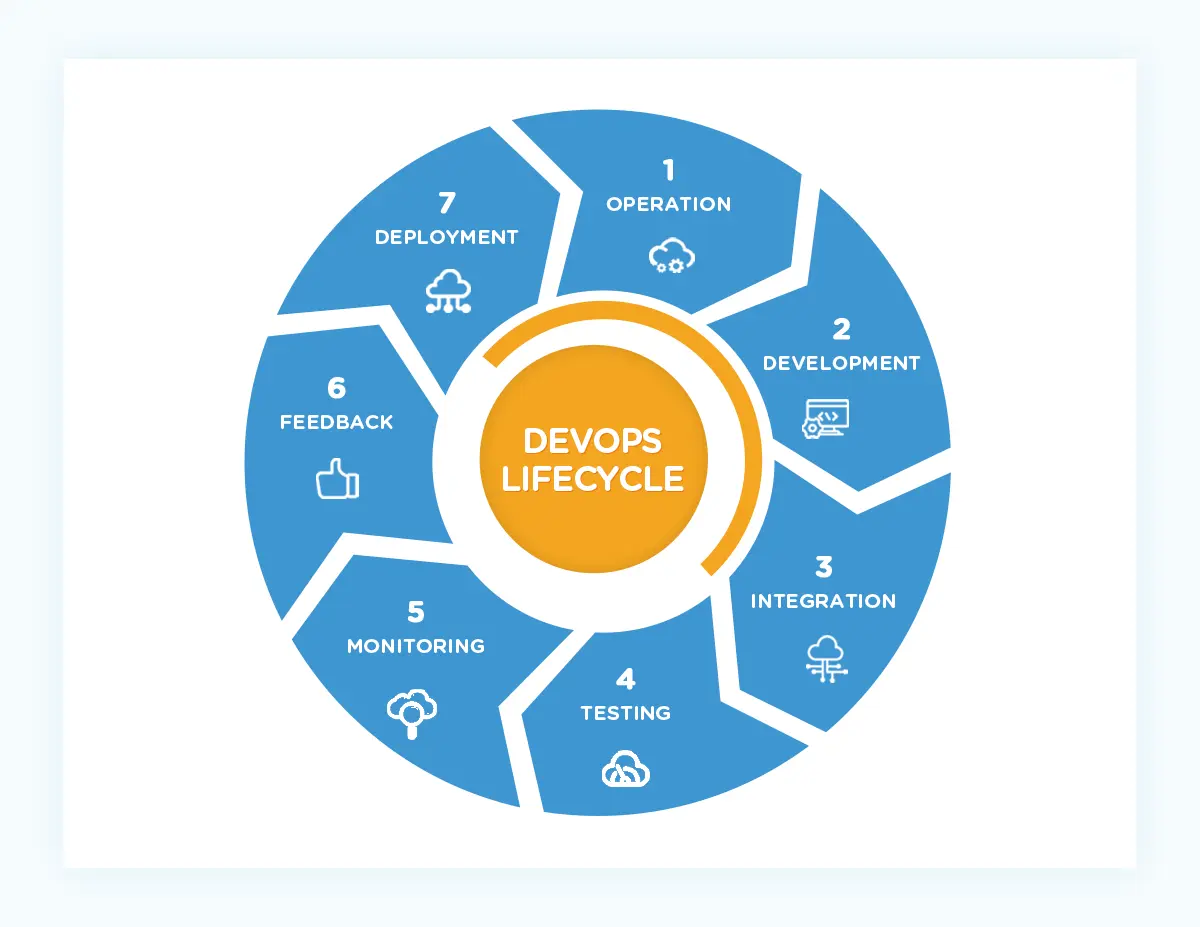
A typical DevOps day involves a continuous cycle of development, testing, deployment, and operations, often automated and integrated. This includes coding, testing, integrating code changes, deploying to various environments, monitoring performance, and responding to incidents, all with a focus on continuous improvement.
Here's a more detailed look at a typical DevOps workflow:
.
1. Development & Planning:
.
• Requirements Gathering: Define what needs to be built and what features are needed.
• Planning and Prioritization: Decide on the order in which features will be implemented.
• Coding: Developers write the code to implement new features or fix bugs.
.
2. Continuous Integration (CI):
.
• Automated Builds: Code is automatically built and tested to ensure it integrates correctly.
• Code Reviews: Code is reviewed by other developers for quality and adherence to standards.
• Feedback Loops: Developers receive immediate feedback on any issues or problems with their code.
.
3. Continuous Testing (CT):
.
• Automated Testing: Tests are run on code to ensure it functions correctly and meets quality standards.
• Types of Tests: Includes unit tests, integration tests, and acceptance tests.
• Feedback and Iteration: Test results are used to identify and fix any issues in the code.
.
4. Continuous Deployment (CD):
.
• Automated Deployment: Code is automatically deployed to different environments (staging, production).
• Deployment Automation: Tools are used to automate the deployment process, reducing human error and increasing speed.
• Monitoring and Feedback: Performance of the deployed code is continuously monitored, and any issues are reported.
.
5. Continuous Operations (CO):
.
• Monitoring: Systems and applications are continuously monitored for performance, availability, and security.
• Incident Response: DevOps teams respond to incidents, such as outages or performance problems, quickly and efficiently.
• Automation: Many operational tasks are automated, including deployment, monitoring, and incident response.
.
6. Continuous Improvement (CI):
.
• Learning and Improvement: DevOps teams continuously evaluate their processes and tools to identify areas for improvement.
• Feedback and Iteration: Feedback from users, developers, and operations teams is used to improve the software and processes.
• Automation and Standardization: DevOps strives to automate as many tasks as possible and standardize processes to increase efficiency and reduce error.
.
